Rise of the Supergrid: DC Electricity Now Flows Across Continents
January 31, 2017
Transmitting power over thousands of kilometres requires a new electricity infrastructure, asserts The Economist in a recent article.
Here’s an example already in the works: later this year construction may begin on a 1,100km long cable — the Plains and Eastern Line — between Oklamoma and western Tennessee. The line will carry 4,000MW, almost enough electricity to power Greater London. It will use direct current (DC) rather than the alternating current (AC) that electricity grids usually employ, and will run at a higher voltage than such grids use — 600,000 volts, rather than 400,000.
This long-distance ultra-high-voltage direct-current (UHVDC) connector will be the first of its kind in America, says The Economist, and is a possible solution to problems everywhere: how to transport green power generated by fixed sources, such as wind, solar and hydroelectric, to power stations located elsewhere.
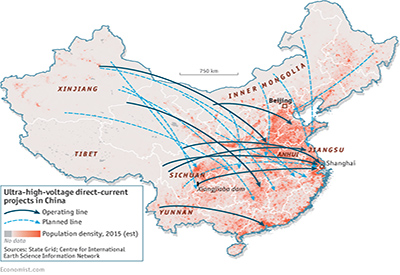
Transmitting power over thousands of kilometres requires a different sort of technology from the AC now used to transmit it tens or hundreds of kilometres through local grids, notes The Economist. In China, Europe and Brazil, as well as in Oklahoma, a new kind of electrical infrastructure is being built to do this: DC “supergrids.”
Why AC won’t work
One of the historical advantages of AC is that transformers allows AC voltages to be increased after generation, for more efficient transmission over longish distances, and then decreased again at the other end of the line, to supply customers with power. By the time a solution was found for DC, AC was already entrenched. However, AC’s advantage dissipates over transcontinental distances. To push the current farther, AC employs (and wastes) an ever-increasing amount of energy in the task of squeezing through the line, explains The Economist.
Direct current does not have this problem. Furthermore, long-distance DC electrical lines are cheaper to build because the footprint of their pylons is smaller and each DC cable can carry much more power than an equivalent AC cable. Although DC lines require expensive thyristors — the equivalent to AC transformers — they allow ultra-high voltages required for more efficient transcontinental transmission.
So far China is further ahead than other countries, and is now introducing this ultra-high voltage direct current (UHVDC) technology elsewhere, such as Spain and Brazil. However, China is not alone. In India, ABB, Siemens and General Electric are building a second UHVDC line that, like the first, will transmit 6,000MW.
Some utilities, such as 50Hertz in northeast Germany, are now considering UHVDC lines for moving power over relatively short distances. That’s because UHVDC lines are point-to-point, unlike traditional AC lines, which are typically part of a grid. Power in one grid can spread into other connected grids, disusing the power and posing problems for the other grids.
The head of 50Hertz expects that within 10 years UHVDC will stretch from the north of Sweden down to Bavaria. After that, perhaps the emergence of a UHVDC grid in Europe in which the lines actually interconnect with each other.
This would require special circuit breakers to isolate faulty cables, and new switch gear, but would make the use of renewable-energy sources much easier.
Such projects—which are transnational as well as transcontinental—carry risks beyond the merely technological, says The Economist. Outsourcing electricity generation to a neighbouring country requires trust in the neighbour’s political stability and good faith. If trust could be established, Earth’s wind-blasted and sun-scorched deserts could provide humanity with a lot of clean, cheap power. The technology to do so is there. But is the political will?
Read the full article: http://www.economist.com/news/science-and-technology/21714325-transmitting-power-over-thousands-kilometres-requires-new-electricity.